Challenge Description
This malware reversing challenge from HackTheBox presents us with an active malware (managed active). This is a Windows based .exe file and a .pdb file.
Challenge Details:
- Difficulty: Hard
- Category: Malware Reversing
- Points: 2100
Initial Analysis
Upon downloading we have the following files : -
- AetherDesk-v74-77.exe
- AetherDesk-v74-77.pdb
- DANGER.txt (This contains the warning about it only)
The CTF had the following Questions which has to be answered and these answers were considered as the flags. The answer for the following 10 questions are the flags.
- During execution, the malware initializes the COM library on its main thread. Based on the imported functions, which DLL is responsible for providing this functionality? (filename.ext)
- Which GUID is used by the binary to instantiate the object containing the data and code for execution? (********-****-****-************)
- Which .NET framework feature is the attacker using to bridge calls between a managed .NET class and an unmanaged native binary? (string)
- Which Opcode in the disassembly is responsible for calling the first function from the managed code? (** ** **)
- Identify the multiplication and addition constants used by the binary's key generation algorithm for decryption. (*,**h)
- Which Opcode in the disassembly is responsible for calling the decryption logic from the managed code? ( ** ** ** )
- Which Win32 API is being utilized by the binary to resolve the killswitch domain name? (string)
- Which network-related API does the binary use to gather details about each shared resource on a server? (string)
- Which Opcode is responsible for running the encrypted payload? ( ** ** **)
- Find → Block → Flag: Identify the killswitch domain, spawn the Docker to block it, and claim the flag. (HTB{*******_*********_********_*****})
Step-By-Step Solution
Question 1: During execution, the malware initializes the COM library on its main thread. Based on the imported functions, which DLL is responsible for providing this functionality? (filename.ext)
This question I answered directly as ole32.dll is the primary COM Library. In order to verify this, we can use tool CFF explorer.
Open CFF Explorer, go to the Imports and there you will find the two libraries of COM. However, for initializing the COM library on the main thread ole32.dll is utilized.

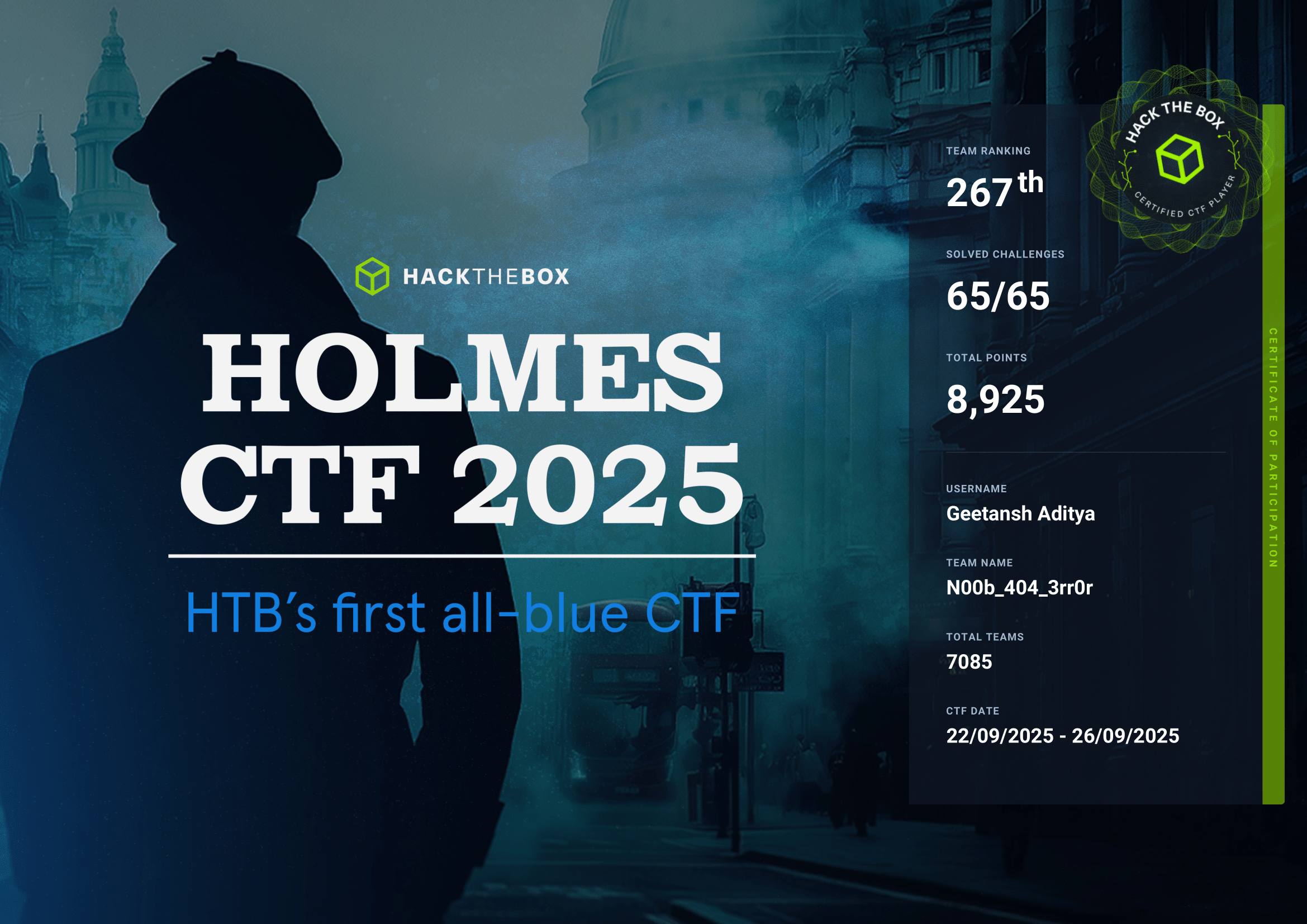
Question 2 : Which GUID is used by the binary to instantiate the object containing the data and code for execution?(********-****-****-************)
For finding this out, I utilized a Ghidra. But you can use anything like BinaryNinja or IDA Pro. In the decompiled view of the main function, you will find the GUID which was used to instantiate.
Question 3: Which .NET framework feature is the attacker using to bridge calls between a managed .NET class and an unmanaged native binary? (string)
Upon reading the code, we came across CoCreateInstance, OleRun, and QueryInterface. I tried to look for it a and found that all of these are from the COM library.
So I searched on google for “COM library api for call between .NET class and unmanaged code” and found the resource Link from Microsoft.
Upon reading you can easily find out the answer.
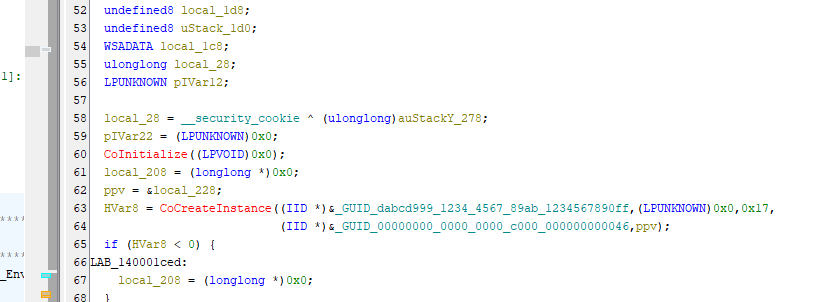
Question 4: Which Opcode in the disassembly is responsible for calling the first function from the managed code? (** ** **)
Now, I want you to focus on this part. Upon reading the code slightly, you will find out that the first time the managed code i.e. the call happened to the .NET happened at the line 87. And the corresponding opcode for that call is ff 50 68 .
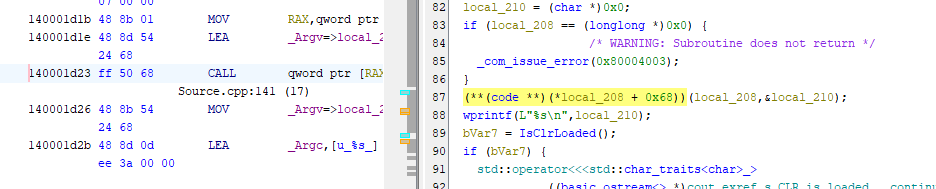
Question 5: Identify the multiplication and addition constants used by the binary's key generation algorithm for decryption. (*, **h)
Once again, upon reading the main function you will find the logic for the decryption. And you will find the corresponding constants. In the format of the answer (, *h), h means hexadecimal. so we need the hex values.
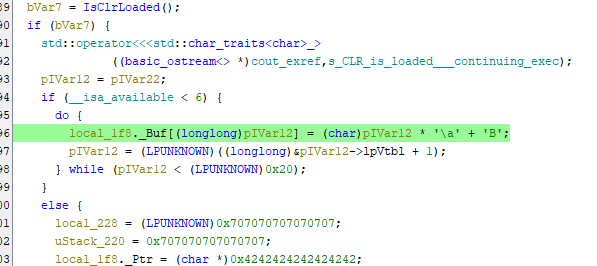
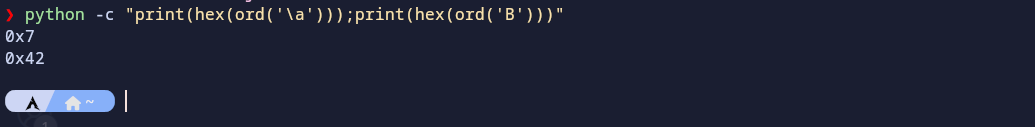
In the image we can see the line:
local_1f8._Buf[(longlong)pIVar12] = (char)pIVar12 * '\a' + 'B';
Here, \a and B are the constants that are used for the multiplication and addition respectively. Converting them to their ASCII values we find : -
python -c "print(hex(ord('\a')));print(hex(ord('B')))"
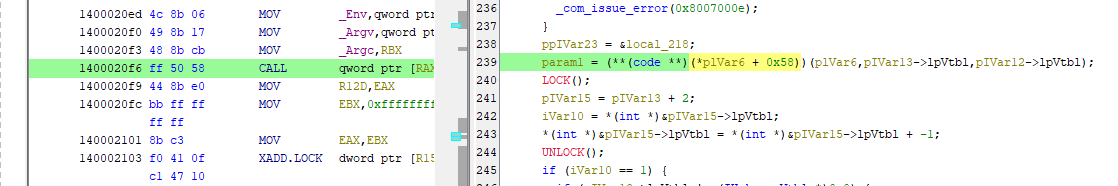
Question 6: Which Opcode in the disassembly is responsible for calling the decryption logic from the managed code? (** ** **)
Once again, you will find the decryption logic in the main function. This is very straightforward answer.
Question 7: Which Win32 API is being utilized by the binary to resolve the killswitch domain name? (string)
So I found the following code block : -
if (pIVar15 != (LPUNKNOWN)0x0) {
pIVar15->lpVtbl = (IUnknownVtbl *)0x0;
pIVar15[1].lpVtbl = (IUnknownVtbl *)0x0;
pIVar15[2].lpVtbl = (IUnknownVtbl *)0x0;
pIVar15[1].lpVtbl = (IUnknownVtbl *)0x0;
*(undefined4 *)&pIVar15[2].lpVtbl = 1;
local_1f8._Ptr = (char *)pIVar15;
pIVar14 = (IUnknownVtbl *)_com_util::ConvertStringToBSTR("KXgmYHMADxsV8uHiuPPB3w==");
pIVar15->lpVtbl = pIVar14;
pIVar13 = pIVar15;
}
When I found this string KXgmYHMADxsV8uHiuPPB3w==. So I tried to check where its called and found a function named getaddrinfo which is used for the DNS resolution. The decoded string is supplied to this getaddrinfo which is an API from the Win32.
Question 8: Which network-related API does the binary use to gather details about each shared resource on a server? (string)
At the end, the main function was calling another function called ScanAndSpread() . I tried to see the decompiled view of the function ScanAndSpread and there I found NetShareEnum which is a Windows API that retrieves information about each shared resource on the server.
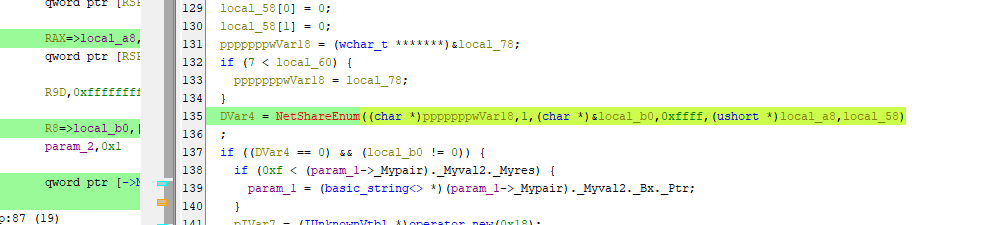
Question 9: Which Opcode is responsible for running the encrypted payload? (** ** **)
In the same ScanAndSpread function, we find an encrypted blob. And then I started looking where its been called. And just few lines below this, the call was made and we can find the opcode in the Listing view.
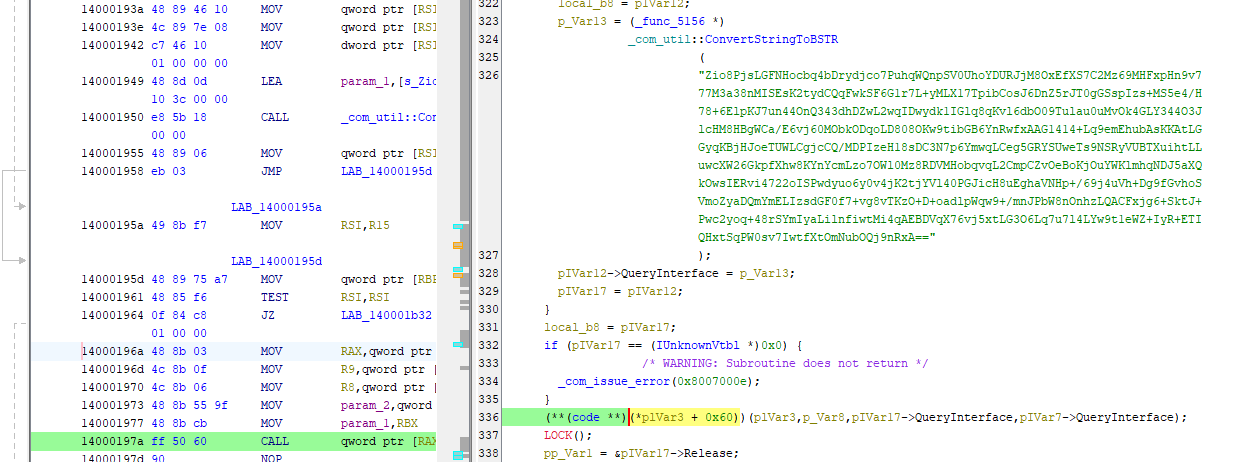
Question 10: Find → Block → Flag: Identify the killswitch domain, spawn the Docker to block it, and claim the flag.(HTB{*******_*********_********_*****})
As we have already identified the kill switch in the Question 7 we have the encrypted string as KXgmYHMADxsV8uHiuPPB3w== .
Now we have to decrypt it. We have all the information required at our disposal. We need the xor key for decrypting the killswitch domain. And the logic for generating the key was given as the answer for Question 5.
key_array = []
for i in range(32):
key_array.append(format((i * 7 + ord('B')) & 0xff, '02x'))
print(''.join(key_array))
From the above code, we get the key as following : -
424950575e656c737a81888f969da4abb2b9c0c7ced5dce3eaf1f8ff060d141b
Now we will use the CyberChef for decryption.
Input = KXgmYHMADxsV8uHiuPPB3w==
Recipe : - From Base64 → XOR with our output hex key
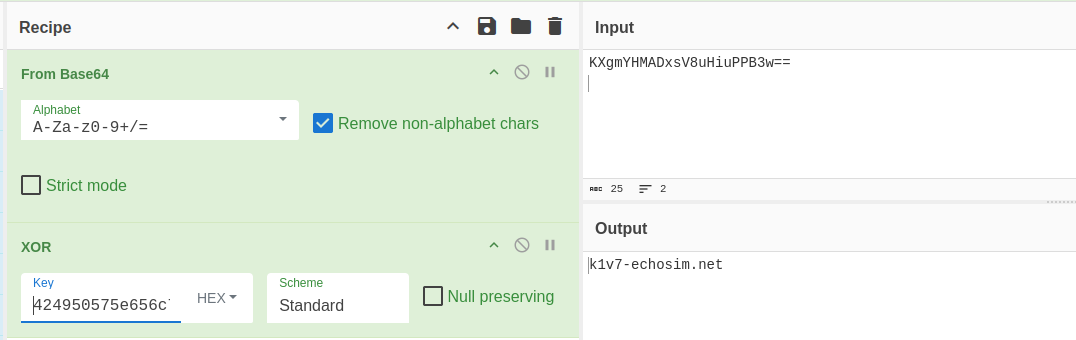
We get k1v7-echosim.net but this is not the answer. Now spawn the docker container and you will reach a DNS Management Dashboard. But the domain here and submit and you will receive the final flag.
Key Learning
The kill-switch was a really nice touch in this challenge as it was from the WannaCry concept. And the final flag uses the word “Eternal” which is from the “EternalBlue” exploit. I really liked this touch. However, the overall difficulty of this challenge should be easy to medium. It was easy once you have a bit of understanding about code reading.
Author’s Note
I am Geetansh Aditya and I participated in this CTF with Andrew Crotty, Devin Plato, Jason C Scribner and Luigi "Vibes" Rulloda. Together we managed 267/7085 teams.
If you’d like to connect, collaborate, or discuss research with me:
- 🌐 LinkedIn
- 📩 Contact me through my website
I don’t just stop at reversing binaries — I work across the spectrum of cybersecurity, from red teaming to blue team forensics.
Happy Reversing and Happy Hacking!!!